Knee pain is a common health issue among athletes and the general population alike. Although symptoms of knee pain can be debilitating and frustrating, knee pain is often a very treatable health issue. The knee is a complex structure made up of three bones: the lower section of the thighbone, the upper region of the shinbone, and the kneecap.
Powerful soft tissues, such as the tendons and ligaments of the knee as well as the cartilage beneath the kneecap and between the bones, hold these structures together in order to stabilize and support the knee. However, a variety of injuries and/or conditions can ultimately lead to knee pain. The purpose of the article below is to evaluate patients with knee pain.
Table of Contents
Abstract
Family physicians frequently encounter patients with knee pain. Accurate diagnosis requires a knowledge of knee anatomy, common pain patterns in knee injuries, and features of frequently encountered causes of knee pain, as well as specific physical examination skills. The history should include characteristics of the patient’s pain, mechanical symptoms (locking, popping, giving way), joint effusion (timing, amount, recurrence), and mechanism of injury. The physical examination should include careful inspection of the knee, palpation for point tenderness, assessment of joint effusion, range-of-motion testing, evaluation of ligaments for injury or laxity, and assessment of the menisci. Radiographs should be obtained in patients with isolated patellar tenderness or tenderness at the head of the fibula, inability to bear weight or flex the knee to 90 degrees, or age greater than 55 years. (Am Fam Physician 2003; 68:907-12. Copyright© 2003 American Academy of Family Physicians.)
Introduction
Knee pain accounts for approximately one-third of musculoskeletal problems seen in primary care settings. This complaint is most prevalent in physically active patients, with as many as 54 percent of athletes having some degree of knee pain each year.1 Knee pain can be a source of significant disability, restricting the ability to work or perform activities of daily living.
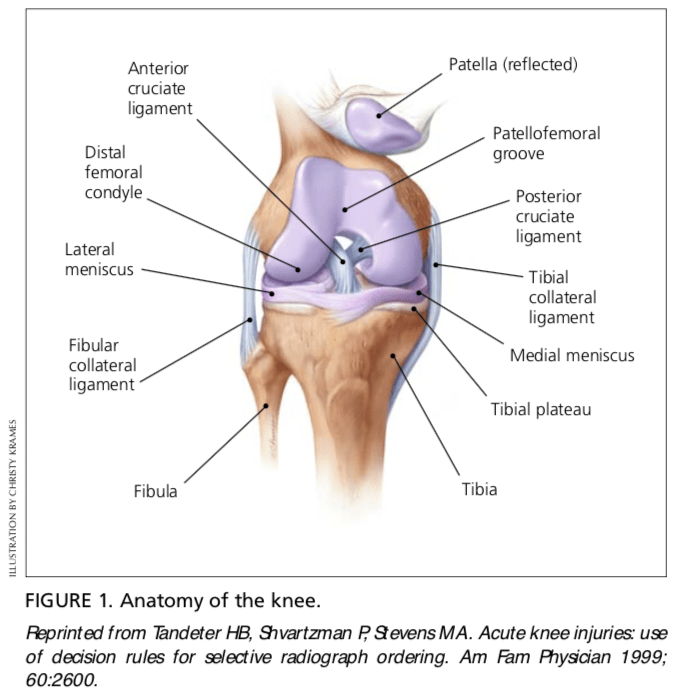
The knee is a complex structure (Figure 1),2 and its evaluation can present a challenge to the family physician. The differential diagnosis of knee pain is extensive but can be narrowed with a detailed history, a focused physical examination and, when indicated, the selective use of appropriate imaging and laboratory studies. Part I of this two-part article provides a systematic approach to evaluating the knee, and part II3 discusses the differential diagnosis of knee pain.
History
Pain Characteristics
The patient’s description of knee pain is helpful in focusing the differential diagnosis.4 It is important to clarify the characteristics of the pain, including its onset (rapid or insidious), location (anterior, medial, lateral, or posterior knee), duration, severity, and quality (e.g., dull, sharp, achy). Aggravating and alleviating factors also need to be identified. If knee pain is caused by an acute injury, the physician needs to know whether the patient was able to continue activity or bear weight after the injury or was forced to cease activities immediately.

Mechanical Symptoms
The patient should be asked about mechan- ical symptoms, such as locking, popping, or giving way of the knee. A history of locking episodes suggests a meniscal tear. A sensation of popping at the time of injury suggests liga- mentous injury, probably complete rupture of a ligament (third-degree tear). Episodes of giving way are consistent with some degree of knee instability and may indicate patellar sub- luxation or ligamentous rupture.
Effusion
The timing and amount of joint effusion are important clues to the diagnosis. Rapid onset (within two hours) of a large, tense effusion suggests rupture of the anterior cru- ciate ligament or fracture of the tibial plateau with resultant hemarthrosis, whereas slower onset (24 to 36 hours) of a mild to moderate effusion is consistent with meniscal injury or ligamentous sprain. Recurrent knee effusion after activity is consistent with meniscal injury.
Mechanism of Injury
The patient should be questioned about specific details of the injury. It is important to know if the patient sustained a direct blow to the knee, if the foot was planted at the time of injury, if the patient was decelerating or stopping suddenly, if the patient was landing from a jump, if there was a twisting component to the injury, and if hyperextension occurred.
A direct blow to the knee can cause serious injury. The anterior force applied to the proximal tibia with the knee in flexion (e.g., when the knee hits the dashboard in an automobile accident) can cause injury to the posterior cruciate ligament. The medial collateral ligament is most commonly injured as a result of direct lateral force to the knee (e.g., clipping in football); this force creates a val- gus load on the knee joint and can result in rupture of the medial collateral ligament. Conversely, a medial blow that creates a varus load can injure the lateral collateral ligament.
Noncontact forces also are an important cause of knee injury. Quick stops and sharp cuts or turns create significant deceleration forces that can sprain or rupture the anterior cruciate ligament. Hyperextension can result in injury to the anterior cruciate ligament or posterior cruciate ligament. Sudden twisting or pivoting motions create shear forces that can injure the meniscus. A combination of forces can occur simultaneously, causing injury to multiple structures.
Medical History
A history of knee injury or surgery is important. The patient should be asked about previous attempts to treat knee pain, including the use of medications, supporting devices, and physical therapy. The physician also should ask if the patient has a history of gout, pseudogout, rheumatoid arthritis, or other degenerative joint diseases.

Knee pain is a common health issue which can be caused by sports injuries, automobile accident injuries, or by an underlying health issue, such as arthritis. The most common symptoms of knee injury include pain and discomfort, swelling, inflammation and stiffness. Because treatment for knee pain varies according to the cause, it’s essential for the individual to receive proper diagnosis for their symptoms. Chiropractic care is a safe and effective, alternative treatment approach which can help treat knee pain, among other health issues.
Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Physical Examination
Inspection and Palpation
The physician begins by comparing the painful knee with the asymptomatic knee and inspecting the injured knee for erythema, swelling, bruising, and discoloration. The mus- culature should be symmetric bilaterally. In particular, the vastus medialis obliquus of the quadriceps should be evaluated to determine if it appears normal or shows signs of atrophy.
The knee is then palpated and checked for pain, warmth, and effusion. Point tenderness should be sought, particularly at the patella, tibial tubercle, patellar tendon, quadriceps tendon, anterolateral and anteromedial joint line, medial joint line, and lateral joint line. Moving the patient’s knee through a short arc of motion helps identify the joint lines. Range of motion should be assessed by extending and flexing the knee as far as possible (normal range of motion: extension, zero degrees; flex- ion, 135 degrees).5
Patellofemoral Assessment
An evaluation for effusion should be conducted with the patient supine and the injured knee in extension. The suprapatellar pouch should be milked to determine whether an effusion is present.
Patellofemoral tracking is assessed by observing the patella for smooth motion while the patient contracts the quadriceps muscle. The presence of crepitus should be noted during palpation of the patella.
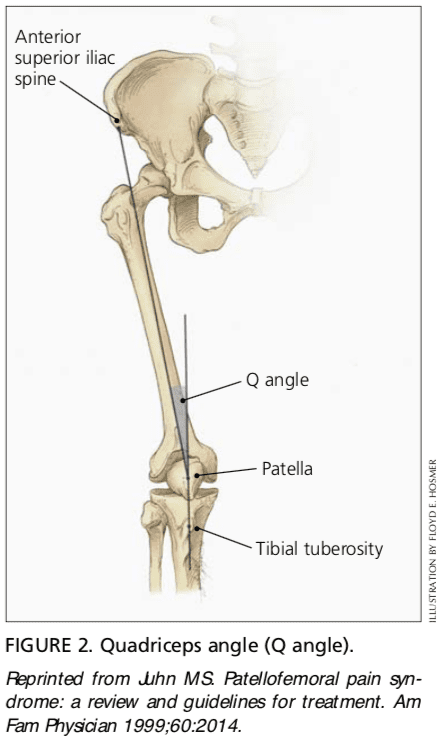
The quadriceps angle (Q angle) is determined by drawing one line from the anterior superior iliac spine through the center of the patella and a second line from the center of the patella through the tibial tuberosity (Figure 2).6 A Q angle greater than 15 degrees is a predisposing factor for patellar subluxation (i.e., if the Q angle is increased, forceful contraction of the quadriceps muscle can cause the patella to sublux laterally).
A patellar apprehension test is then performed. With fingers placed at the medial aspect of the patella, the physician attempts to sublux the patella laterally. If this maneuver reproduces the patient’s pain or a giving-way sensation, patellar subluxation is the likely cause of the patient’s symptoms.7 Both the superior and inferior patellar facets should be palpated, with the patella subluxed first medially and then laterally.
Cruciate Ligaments
Anterior Cruciate Ligament. For the anterior drawer test, the patient assumes a supine position with the injured knee flexed to 90 degrees. The physician fixes the patient’s foot in slight external rotation (by sitting on the foot) and then places thumbs at the tibial tubercle and fingers at the posterior calf. With the patient’s hamstring muscles relaxed, the physician pulls anteriorly and assesses anterior displacement of the tibia (anterior drawer sign).
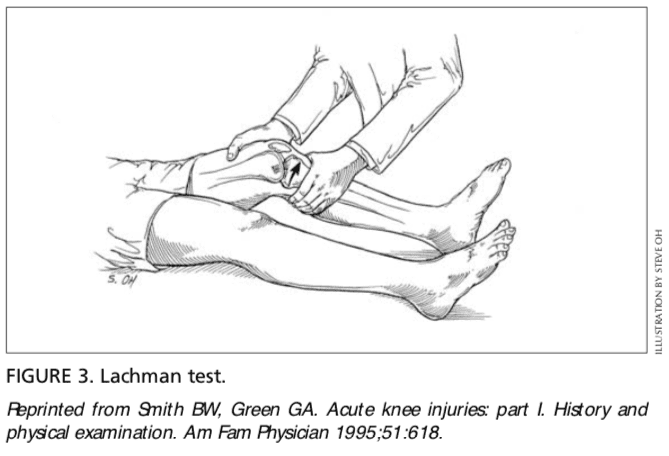
The Lachman test is another means of assessing the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (Figure 3).7 The test is performed with the patient in a supine position and the injured knee flexed to 30 degrees. The physician stabilizes the distal femur with one hand, grasps the proximal tibia in the other hand, and then attempts to sublux the tibia anteriorly. Lack of a clear end point indicates a positive Lachman test.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament. For the posterior drawer test, the patient assumes a supine position with knees flexed to 90 degrees. While standing at the side of the examination table, the physician looks for posterior displacement of the tibia (posterior sag sign).7,8 Next, the physician fixes the patient’s foot in neutral rotation (by sitting on the foot), positions thumbs at the tibial tubercle, and places fingers at the posterior calf. The physician then pushes posteriorly and assesses for posterior displacement of the tibia.
Collateral Ligaments
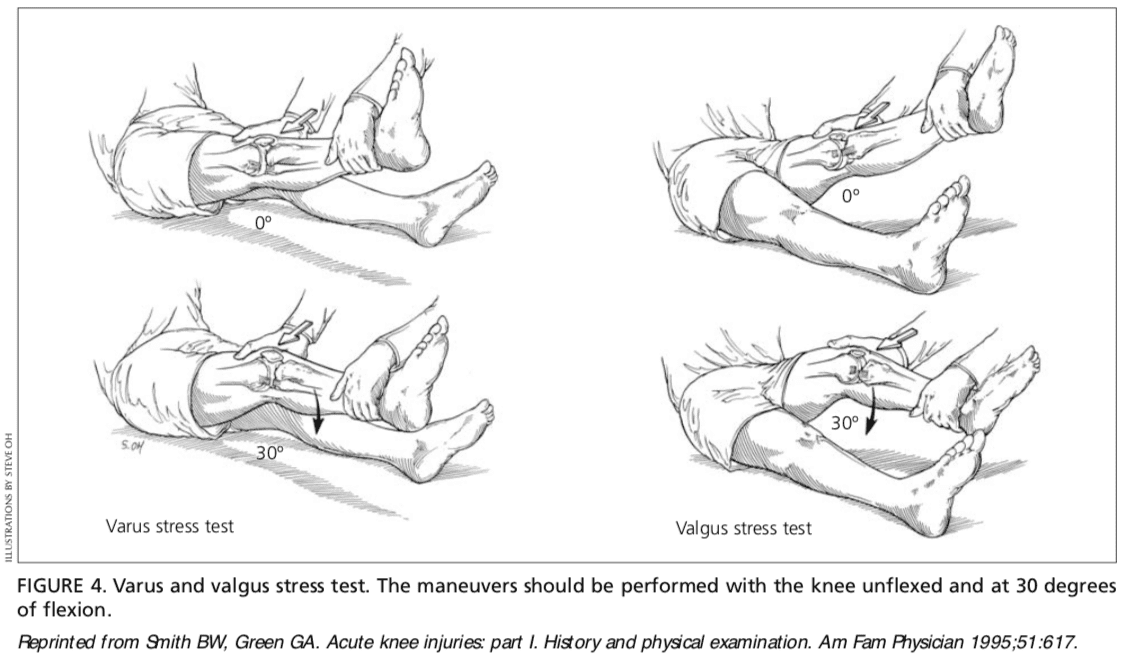
Medial Collateral Ligament. The valgus stress test is performed with the patient’s leg slightly abducted. The physician places one hand at the lateral aspect of the knee joint and the other hand at the medial aspect of the distal tibia. Next, valgus stress is applied to the knee at both zero degrees (full extension) and 30 degrees of flexion (Figure 4)7. With the knee at zero degrees (i.e., in full extension), the posterior cruciate ligament and the articulation of the femoral condyles with the tibial plateau should stabilize the knee; with the knee at 30 degrees of flexion, application of valgus stress assesses the laxity or integrity of the medial collateral ligament.
Lateral Collateral Ligament. To perform the varus stress test, the physician places one hand at the medial aspect of the patient’s knee and the other hand at the lateral aspect of the distal fibula. Next, varus stress is applied to the knee, first at full extension (i.e., zero degrees), then with the knee flexed to 30 degrees (Figure 4).7 A firm end point indicates that the collateral ligament is intact, whereas a soft or absent end point indicates complete rupture (third-degree tear) of the ligament.
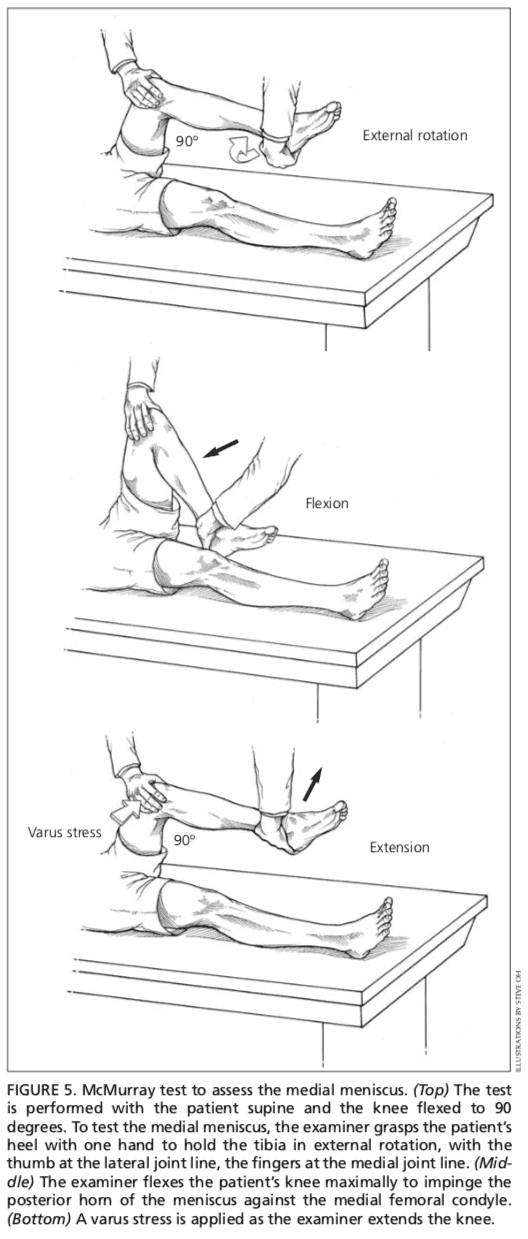
Menisci
Patients with injury to the menisci usually demonstrate tenderness at the joint line. The McMurray test is performed with the patient lying supine9 (Figure 5). The test has been described variously in the literature, but the author suggests the following technique.
The physician grasps the patient’s heel with one hand and the knee with the other hand. The physician’s thumb is at the lateral joint line, and fingers are at the medial joint line. The physician then flexes the patient’s knee maximally. To test the lateral meniscus, the tibia is rotated internally, and the knee is extended from maximal flexion to about 90 degrees; added compression to the lateral meniscus can be produced by applying valgus stress across the knee joint while the knee is being extended. To test the medial meniscus, the tibia is rotated externally, and the knee is extended from maximal flexion to about 90 degrees; added compression to the medial meniscus can be produced by placing varus stress across the knee joint while the knee is degrees of flexion. A positive test produces a thud or a click, or causes pain in a reproducible portion of the range of motion.
Because most patients with knee pain have soft tissue injuries, plain-film radiographs generally are not indicated. The Ottawa knee rules are a useful guide for ordering radiographs of the knee10,11.
If radiographs are required, three views are usually sufficient: anteroposterior view, lateral view, and Merchant’s view (for the patellofemoral joint).7,12 Teenage patients who report chronic knee pain and recurrent knee effusion require a notch or tunnel view (posteroanterior view with the knee flexed to 40 to 50 degrees). This view is necessary to detect radiolucencies of the femoral condyles (most commonly the medial femoral condyle), which indicate the presence of osteochondritis dissecans.13
Radiographs should be closely inspected for signs of fracture, particularly involving the patella, tibial plateau, tibial spines, proximal fibula, and femoral condyles. If osteoarthritis is suspected, standing weight-bearing radiographs should be obtained.
Laboratory Studies
The presence of warmth, exquisite tenderness, painful effusion, and marked pain with even slight range of motion of the knee joint is consistent with septic arthritis or acute inflammatory arthropathy. In addition to obtaining a complete blood count with differential and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), arthro- centesis should be performed. The joint fluid should be sent to a laboratory for a cell count with differential, glucose and protein measure- ments, bacterial culture and sensitivity, and polarized light microscopy for crystals.
Because a tense, painful, swollen knee may present an unclear clinical picture, arthrocentesis may be required to differentiate simple effusion from hemarthrosis or occult osteochondral fracture.4 A simple joint effusion produces clear, straw-colored transudative fluid, as in a knee sprain or chronic meniscal injury. Hemarthrosis is caused by a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament, a fracture or, less commonly, an acute tear of the outer portion of the meniscus. An osteochondral fracture causes hemarthrosis, with fat globules noted in the aspirate.
Rheumatoid arthritis may involve the knee joint. Hence, serum ESR and rheumatoid factor testing are indicated in selected patients.
The authors indicate that they do not have any conflicts of interest. Sources of funding: none reported.
In conclusion, knee pain is a common health issue which occurs due to a variety of injuries and/or conditions, such as sports injuries, automobile accidents, and arthritis, among other problems. Treatment of knee pain depends largely on the source of the symptoms. Therefore, it is essential for the individual to seek immediate medical attention to receive a diagnosis.
Chiropractic care is an alternative treatment option which focuses on the treatment of a variety of injuries and/or conditions associated with the musculoskeletal and nervous system. The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic and spinal health issues. To discuss the subject matter, please feel free to ask Dr. Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez
1. Rosenblatt RA, Cherkin DC, Schneeweiss R, Hart LG. The content of ambulatory medical care in the United States. An interspecialty comparison. N Engl J Med 1983;309:892-7.
2. Tandeter HB, Shvartzman P, Stevens MA. Acute knee injuries: use of decision rules for selective radiograph ordering. Am Fam Physician 1999;60: 2599-608.
3. Calmbach WL, Hutchens M. Evaluation of patients presenting with knee pain: part II. Differential diag- nosis. Am Fam Physician 2003;68:917-22
4. Bergfeld J, Ireland ML, Wojtys EM, Glaser V. Pin- pointing the cause of acute knee pain. Patient Care 1997;31(18):100-7.
5. Magee DJ. Knee. In: Orthopedic physical assessment. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002:661-763.
6. Juhn MS. Patellofemoral pain syndrome: a review and guidelines for treatment. Am Fam Physician 1999;60:2012-22.
7. Smith BW, Green GA. Acute knee injuries: part I. History and physical examination. Am Fam Physi- cian 1995;51:615-21.
8. Walsh WM. Knee injuries. In: Mellion MB, Walsh WM, Shelton GL, eds. The team physician’s hand- book. 2d ed. St. Louis: Mosby, 1997:554-78.
9. McMurray TP. The semilunar cartilage. Br J Surg 1942;29:407-14.
10. Stiell IG, Wells GA, Hoag RH, Sivilotti ML, Cacciotti TF, Verbeek PR, et al. Implementation of the Ottawa knee rule for the use of radiography in acute knee injuries. JAMA 1997;278:2075-9.
11. Stiell IG, Greenberg GH, Wells GA, McKnight RD, Cwinn AA, Caciotti T, et al. Derivation of a decision rule for the use of radiography in acute knee injuries. Ann Emerg Med 1995;26:405-13.
12. Sartoris DJ, Resnick D. Plain film radiography: rou- tine and specialized techniques and projections. In: Resnick D, ed. Diagnosis of bone and joint disor- ders. 3d ed. Philadelphia: Saunders:1-40.
13. Schenck RC Jr, Goodnight JM. Osteochondritis dis- secans. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1996;78:439-56.

Additional Topic Discussion: Relieving Knee Pain without Surgery
Knee pain is a well-known symptom which can occur due to a variety of knee injuries and/or conditions, including sports injuries. The knee is one of the most complex joints in the human body as it is made-up of the intersection of four bones, four ligaments, various tendons, two menisci, and cartilage. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, the most common causes of knee pain include patellar subluxation, patellar tendinitis or jumper’s knee, and Osgood-Schlatter disease. Although knee pain is most likely to occur in people over 60 years old, knee pain can also occur in children and adolescents. Knee pain can be treated at home following the RICE methods, however, severe knee injuries may require immediate medical attention, including chiropractic care.

EXTRA EXTRA | IMPORTANT TOPIC: Recommended Chiropractor El Paso, TX
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Evaluation of Patients Presenting with Knee Pain: Part I. History, Physical Examination, Radiographs, and Laboratory Tests" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics




 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.