Patellar tendinitis is a common health issue characterized by the inflammation of the tendon which joins the kneecap, or patella, to the shinbone, or tibia. The knee pain associated with this problem may range from mild to severe depending on the circumstances of the knee injury.
Patellar tendinitis, or jumper’s knee, is a well-known sports injury among athletes who play in basketball and volleyball. Among recreational volleyball players, an estimated 14.4 percent of them have jumper’s knee, where the incidence is even higher for professional athletes. An estimated 40 to 50 percent of elite volleyball players have patellar tendinitis.
Table of Contents
Causes of Patellar Tendinitis
Patellar tendinitis is caused by repetitive strain on the knee, most often from overuse in physical activities. Stress can create tears along the tendons which can cause inflammation in the complex structures of the knee.
Other contributing factors of patellar tendinitis include:
- Tight or stiff leg muscles
- Uneven leg muscle strength
- Misaligned toes, ankles, and legs
- Obesity
- Sneakers without enough padding
- Tough playing surfaces
- Chronic health issues that weaken the tendon
Athletes have a higher chance of developing patellar tendinitis because running, jumping, and squatting put more force over the tendon. Running can place a force of as many as five times the body weight on the knees.
Intense physical activity for an extended amount of time has been previously associated with jumper’s knee. A 2014 research study noted that jump frequency was also a significant risk factor for amateur players.
Symptoms of Patellar Tendinitis
The initial symptoms of patellar tendinitis include pain, discomfort, and tenderness at the base of the kneecap or patella. Other symptoms of patellar tendinitis may include a burning sensation. For many patients, getting up from a squat or kneeling down can also be particularly debilitating.
The pain associated with patellar tendinitis may be irregular at first, manifesting immediately after participating in physical activities. Damage or injury to the tendon can also make the pain worse. Jumper’s knee can affect regular daily activities, such as climbing stairs or sitting in a vehicle.

Patellar tendinitis, also known as “jumper’s knee”, is a particularly common cause of pain and discomfort in the patellar region of many athletes. While it frequently occurs as a result of repetitive or continuous jumping, research studies have demonstrated that patellar tendinitis may be associated with stiff ankle movements and ankle sprains, among other sports injuries.
Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Patellar Tendinitis Diagnosis
At the start of a consultation, the healthcare professional will first ask the patient about their specific health issue. The doctor will then physically evaluate the patient’s knee, probe for where they are feeling pain, and test the assortment of knee motion by bending and extending the patient’s leg.
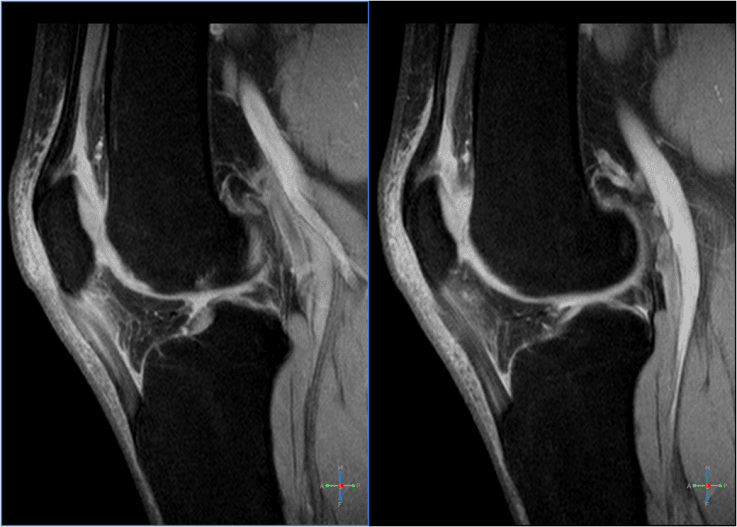
Furthermore, the healthcare professional may additionally order imaging diagnostics to find out if there’s any damage or injury to the tendon or even the bone. These tests can help rule out a broken bone, or fracture. The doctor may use an X-ray to look for a displaced or fractured kneecap, and an MRI or an ultrasound to reveal any harm to the soft tissue.
Patellar Tendinitis Treatment
Treatment for patellar tendinitis depends on the damage or injury to the knee. Conservative steps to reduce pain, such as rest or exercises are generally the first line of treatment. The healthcare professional will usually recommend a span of controlled rest, where they will prevent the patient from engaging in physical activities that put pressure on the knee.
Drugs and/or Medications
The healthcare professional may prescribe over-the-counter drugs and/or medications for short-term pain relief and inflammation reduction.
These can consist of:
- Ibuprofen (Advil)
- Naproxen sodium (Aleve)
- cetaminophen (Tylenol)
If the patient’s symptoms are severe, the healthcare professional may recommend the use of corticosteroid injection in the area around the patellar tendon. This treatment is effective in reducing acute pain.
Another method of utilizing corticosteroid for patellar tendinitis is by spreading the medication over the affected knee and use a low electrical charge to push it through the skin, in a process known as iontophoresis.
Chiropractic Care and Physical Therapy
The goal of chiropractic care and physical therapy for patellar tendinitis is to reduce pain and inflammation, among other symptoms, as well as to strengthen the leg and thigh muscles with stretches and exercises.
If the patient’s symptoms are severe, even while resting, the doctor may recommend that you wear a brace and then use crutches to avoid additional damage or injury to the tendon. If the patient has no painful symptoms, then they can start participating in a physical therapy activities.
A rehabilitation program generally consists of:
- A warm-up interval
- Massage, heat or ice to the knee
- Stretching exercises
- Strengthening exercises
A doctor of chiropractic, or chiropractor, may use ultrasound and electrical stimulation to relieve the patient’s knee pain. A knee brace or taping of the knee might also help reduce pain by supporting the kneecap when engaging in physical activities. The healthcare professional may develop a workout program that may include a series of stretches and exercises.
Surgery
When other treatments are not effective in relieving painful symptoms associated with patellar tendinitis, the doctor may advise surgery to repair the patellar tendon. Traditional surgery involves opening the knee to scrape on the kneecap and tendon. More recently, arthroscopic surgery is used for this particular process. This surgical intervention involves making four small incisions in the knee and it has a shorter recovery time.
The recovery period for surgery varies per procedure. Some surgical intervention advise for immobilization with a cast. Others suggest an immediate rehabilitation program. Regardless of the level of damage and/or injury, it’s essential for patients to seek medical attention for their patellar tendinitis. The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic as well as to spinal injuries and conditions. To discuss the subject matter, please feel free to ask Dr. Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez

Additional Topic Discussion: Relieving Knee Pain without Surgery
Knee pain is a well-known symptom which can occur due to a variety of knee injuries and/or conditions, including sports injuries. The knee is one of the most complex joints in the human body as it is made-up of the intersection of four bones, four ligaments, various tendons, two menisci, and cartilage. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, the most common causes of knee pain include patellar subluxation, patellar tendinitis or jumper’s knee, and Osgood-Schlatter disease. Although knee pain is most likely to occur in people over 60 years old, knee pain can also occur in children and adolescents. Knee pain can be treated at home following the RICE methods, however, severe knee injuries may require immediate medical attention, including chiropractic care.

EXTRA EXTRA | IMPORTANT TOPIC: Knee Injury Treatment
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "What is Patellar Tendinitis?" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, and focuses on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card



 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.