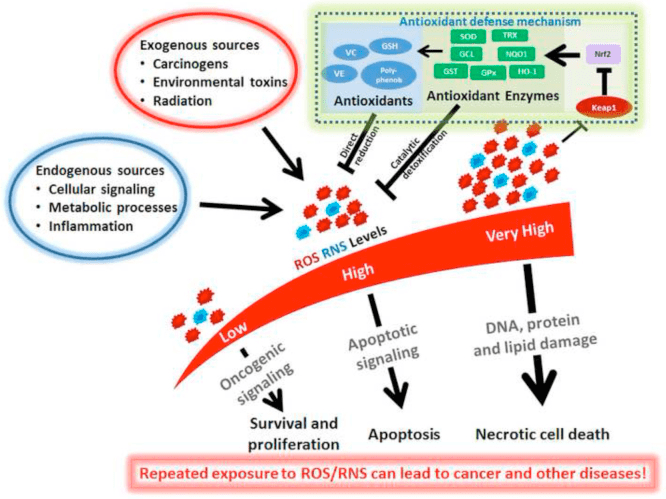
The nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway, best known as Nrf2, is a protective mechanism which functions as a “master regulator” of the human body’s antioxidant response. Nrf2 senses the levels of oxidative stress within the cells and triggers protective antioxidant mechanisms. While Nrf2 activation can have many benefits, Nrf2 “overexpression” can have several risks.
It appears that a balanced degree of NRF2 is essential towards preventing the overall development of a variety of diseases in addition to the general improvement of these health issues. However, NRF2 can also cause complications. The main cause behind NRF2 “overexpression” is due to a genetic mutation or a continuing chronic exposure to a chemical or oxidative stress, among others. Below, we will discuss the downsides of Nrf2 overexpression and demonstrate its mechanisms of action within the human body.
Table of Contents
Cancer
Research studies found that mice that don’t express NRF2 are more inclined to develop cancer in response to physical and chemical stimulation. Similar research studies, however, showed that NRF2 over-activation, or even KEAP1 inactivation, can result in the exacerbation of certain cancers, particularly if those pathways have been interrupted. Overactive NRF2 can occur through smoking, where continuous NRF2 activation is believed to be the cause of lung cancer in smokers. Nrf2 overexpression might cause cancerous cells not to self-destruct, while intermittent NRF2 activation can prevent cancerous cells from triggering toxin induction.
Additionally, because NRF2 overexpression increases the human body’s antioxidant ability to function beyond redox homeostasis, this boosts cell division and generates an unnatural pattern of DNA and histone methylation. This can ultimately make chemotherapy and radiotherapy less effective against cancer. Therefore, limiting NRF2 activation with substances like DIM, Luteolin, Zi Cao, or salinomycin could be ideal for patients with cancer although Nrf2 overactivation should not be considered to be the only cause for cancer. Nutrient deficiencies can affect genes, including NRF2. This might be one way as to how deficiencies contribute to tumors.
Liver
The overactivation of
Heart
While the acute overexpression of Nrf2 may have its benefits, continuous overexpression of NRF2 may cause long-term harmful effects on the heart, such as cardiomyopathy. NRF2 expression can be increased through high levels of cholesterol, or the activation of HO-1. This is believed to be the reason why
Vitiligo
NRF2 overexpression has also been demonstrated to inhibit the capability to repigment in vitiligo as it might obstruct
Why NRF2 May Not Function Properly
Hormesis
NRF2 has to be hormetically activated in order to be able to take advantage of its benefits. In other words, Nrf2 shouldn’t trigger every minute or every day, therefore, it’s a great idea to take breaks from it, by way of instance, 5 days on 5 days off or every other day. NRF2 must also accomplish a specific threshold to trigger its hormetic response, where
DJ-1 Oxidation
Protein
This process induces NRF2 activation to expire too fast since DJ-1 is paramount for maintaining balanced levels of NRF2 and preventing them from being broken down in the cell. In case the DJ-1 protein is non-existent or overoxidized,
Chronic Illness
If you have a chronic illness, including CIRS, chronic infections/dysbiosis/SIBO, or heavy metal build up, such as mercury and/or that from root canals, these can obstruct the systems of NRF2 and phase two detoxification. Rather than oxidative stress turning NRF2 into an antioxidant, NRF2 will not trigger and oxidative stress can remain in the cell and cause damage, meaning, there is no antioxidant response. This is a significant reason why many people with CIRS have several sensitivities and reach to numerous factors. Some people believe they may be having a
Treating chronic illness, however, will permit the liver to discharge toxins into the bile, gradually developing the hormetic response of NRF2 activation. If the bile remains toxic and it’s not excreted from the human body, it will reactivate NRF2’s oxidative stress and cause you to feel worse once it’s reabsorbed from the gastrointestinal, or GI, tract. For example, ochratoxin A may block NRF2. Aside from treating the problem, histone deacetylase inhibitors can block the oxidative reaction from a number of the factors which trigger NRF2 activation but it might also prevent NRF2 from
Fish Oil Dysregulation
People with chronic illnesses might have problems with cognitive stress and acetylcholine excitotoxicity, from organophosphate accumulation, which might cause fish oil to create inflammation within the human body. Choline deficiency additionally induces NRF2 activation. Including choline into your diet, (polyphenols, eggs, etc.) can help enhance the effects of cholinergic dysregulation.
What Decreases NRF2?
Decreasing NRF2 overexpression is best for people that have cancer, although it may be beneficial for a variety of other health issues.
Diet, Supplements, and Common Medicines:
- Apigenin (higher doses)
Brucea javanica - Chestnuts
- EGCG (high doses increase NRF2)
- Fenugreek (Trigonelline)
- Hiba (Hinokitiol / β-
thujaplicin ) - High Salt Diet
- Luteolin (Celery, green pepper, parsley, perilla leaf, and chamomile tea – higher doses may increase NRF2 – 40 mg/kg luteolin three times per week )
- Metformin (chronic intake)
- N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC, by blocking the oxidative response, esp at high doses)
- Orange Peel (have
polymethoxylated flavonoids) - Quercetin (higher doses may increase NRF2 – 50 mg/kg/d quercetin)
- Salinomycin (drug)
- Retinol (all-trans retinoic acid)
- Vitamin C when combined with Quercetin
- Zi Cao (Purple
Gromwel has Shikonin/Alkannin)
Pathways and Other:
- Bach1
- BET
- Biofilms
- Brusatol
- Camptothecin
- DNMT
- DPP-23
- EZH2
- Glucocorticoid Receptor signaling (Dexamethasone and Betamethasone as well)
- GSK-3β (regulatory feedback)
- HDAC activation?
- Halofuginone
- Homocysteine (ALCAR can reverse this homocysteine induce low levels of NRF2)
- IL-24
- Keap1
- MDA-7
- NFκB
- Ochratoxin A(
aspergillus andpencicllium species) - Promyelocytic leukemia protein
- p38
- p53
- p97
- Retinoic acid receptor alpha
- Selenite
- SYVN1 (Hrd1)
- STAT3 inhibition (such as Cryptotanshinone)
- Testosterone (and Testosterone propionate, although TP intranasally may increase NRF2)
- Trecator (Ethionamide)
- Trx1 (via reduction of Cys151 in Keap1 or of Cys506 in the NLS region of Nrf2)
- Trolox
- Vorinostat
- Zinc Deficiency (makes it worse in the brain)
Nrf2 Mechanism Of Action
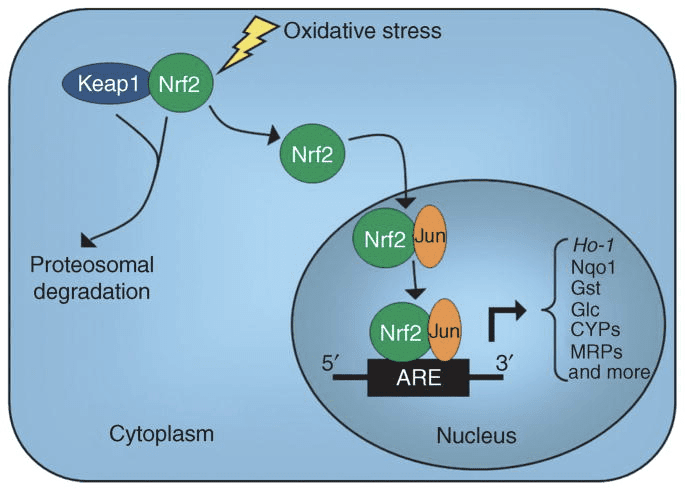
Oxidative stress triggers through CUL3 where NRF2 from KEAP1, a negative inhibitor, subsequently enters the nucleus of these cells, stimulating the transcription of the AREs, turning sulfides into disulfides, and turning them into more antioxidant genes, leading to the upregulation of antioxidants, such as GSH, GPX, GST, SOD, etc.. The rest of these can be seen in the list below:
- Increases AKR
- Increases ARE
- Increases ATF4
- Increases Bcl-xL
- Increases Bcl-2
- Increases BDNF
- Increases BRCA1
- Increases c-Jun
- Increases CAT
- Increases cGMP
- Increases CKIP-1
- Increases CYP450
- Increases Cul3
- Increases GCL
- Increases GCLC
- Increases GCLM
- Increases GCS
- Increases GPx
- Increases GR
- Increases GSH
- Increases GST
- Increases HIF1
- Increases HO-1
- Increases HQO1
- Increases HSP70
- Increases IL-4
- Increases IL-5
- Increases IL-10
- Increases IL-13
- Increases K6
- Increases K16
- Increases K17
- Increases mEH
- Increases Mrp2-5
- Increases NADPH
- Increases Notch 1
- Increases NQO1
- Increases PPAR-alpha
- Increases
Prx - Increases p62
- Increases Sesn2
- Increases Slco1b2
- Increases sMafs
- Increases SOD
- Increases Trx
- Increases Txn(d)
- Increases UGT1(A1/6)
- Increases VEGF
- Reduces ADAMTS(4/5)
- Reduces alpha-SMA
- Reduces ALT
- Reduces AP1
- Reduces AST
- Reduces Bach1
- Reduces COX-2
- Reduces DNMT
- Reduces FASN
- Reduces FGF
- Reduces HDAC
- Reduces IFN-γ
- Reduces IgE
- Reduces IGF-1
- Reduces IL-1b
- Reduces IL-2
- Reduces IL-6
- Reduces IL-8
- Reduces IL-25
- Reduces IL-33
- Reduces iNOS
- Reduces LT
- Reduces Keap1
- Reduces MCP-1
- Reduces MIP-2
- Reduces MMP-1
- Reduces MMP-2
- Reduces MMP-3
- Reduces MMP-9
- Reduces MMP-13
- Reduces NfkB
- Reduces NO
- Reduces SIRT1
- Reduces TGF-b1
- Reduces TNF-alpha
- Reduces Tyr
- Reduces VCAM-1
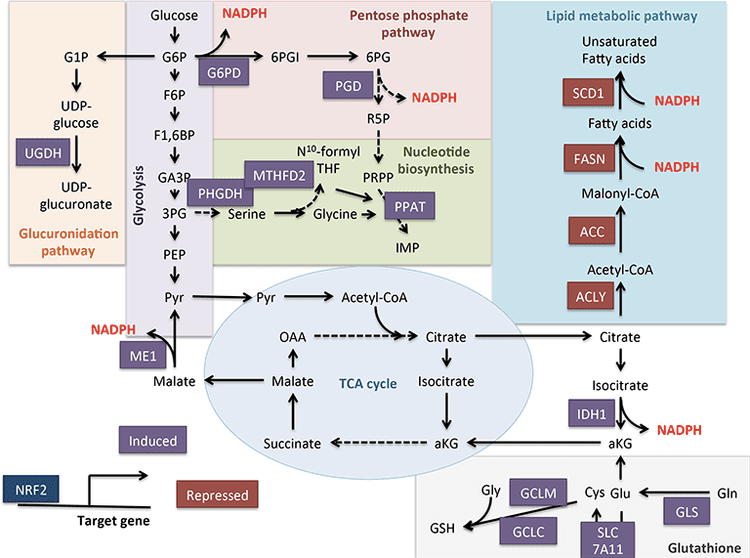
- Encoded from the NFE2L2 gene, NRF2, or nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2, is a transcription factor in the basic leucine zipper, or bZIP, superfamily which utilizes a Cap’n’Collar, or CNC structure.
- It promotes nitric enzymes, biotransformation enzymes, and xenobiotic efflux transporters.
- It is an essential regulator at the induction of the phase II antioxidant and detoxification enzyme genes, which protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and electrophilic attacks.
- During homeostatic conditions, Nrf2 is sequestered in the cytosol through bodily attachment of the N-terminal domain of Nrf2, or the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein or Keap1, also referred to as INrf2 or Inhibitor of Nrf2, inhibiting Nrf2 activation.
- It may also be controlled by mammalian selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1, or TrxR1, which functions as a negative regulator.
- Upon vulnerability to electrophilic stressors, Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1, translocating into the nucleus, where it then heterodimerizes with a range of transcriptional regulatory protein.
- Frequent interactions comprise with those of transcription authorities Jun and Fos, which can be members of the activator protein family of transcription factors.
- After dimerization, these complexes then bind to antioxidant/electrophile responsive components ARE/EpRE and activate transcription, as is true with the Jun-Nrf2 complex, or suppress transcription, much like the Fos-Nrf2 complex.
- The positioning of the ARE, which is triggered or inhibited, will determine which genes are transcriptionally controlled by these variables.
- When ARE is triggered:
- Activation of the synthesis of antioxidants is capable of detoxifying ROS like catalase, superoxide-dismutase, or SOD, GSH-peroxidases, GSH-reductase, GSH-transferase, NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase, or NQO1, Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system, thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase, and HSP70.
- Activation of this GSH synthase permits a noticeable growth of the GSH intracellular degree, which is quite protective.
- The augmentation of this synthesis and degrees of phase II enzymes like UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, N-acetyltransferases, and sulfotransferases.
- The upregulation of HO-1, which is a really protective receptor with a potential growth of CO that in conjunction with NO allows vasodilation of ischemic cells.
- Reduction of iron overload through elevated ferritin and bilirubin as a lipophilic antioxidant. Both the phase II proteins along with the antioxidants are able to fix the chronic oxidative stress and also to revive a normal redox system.
- GSK3β under the management of AKT and PI3K, phosphorylates Fyn resulting in Fyn nuclear localization, which Fyn phosphorylates Nrf2Y568 leading to nuclear export and degradation of Nrf2.
- NRF2 also dampens the TH1/TH17 response and enriches the TH2 response.
- HDAC inhibitors triggered the Nrf2 signaling pathway and up-regulated that the Nrf2 downstream targets HO-1, NQO1, and glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit, or GCLC, by curbing Keap1 and encouraging dissociation of Keap1 from Nrf2, Nrf2 nuclear translocation, and Nrf2-ARE binding.
- Nrf2 includes a half-life of about 20 minutes under basal conditions.
- Diminishing the IKKβ pool through Keap1 binding reduces IκBα degradation and might be the elusive mechanism by which Nrf2 activation is proven to inhibit NFκB activation.
- Keap1 does not always have to be downregulated to get NRF2 to operate, such as chlorophyllin, blueberry, ellagic acid, astaxanthin, and tea polyphenols may boost NRF2 and KEAP1 at 400 percent.
- Nrf2 regulates negatively through the term of stearoyl CoA desaturase, or SCD, and citrate lyase, or CL.
Genetics
KEAP1
rs1048290
- C allele – showed a significant risk for and a protective effect against
drug resistant epilepsy (DRE)
rs11085735 (I’m AC)
- associated with rate of decline of lung function in the LHS
MAPT
rs242561
- T allele – protective allele for Parkinsonian disorders – had stronger NRF2/sMAF binding and was associated with the higher MAPT mRNA levels in 3 different regions in
brain , including cerebellar cortex (CRBL), temporal cortex (TCTX), intralobular white matter (WHMT)
NFE2L2 (NRF2)
rs10183914 (I’m CT)
- T allele – increased levels of Nrf2 protein and delayed
age of onset of Parkinson’s by four years
rs16865105 (I’m AC)
- C allele – had higher risk of Parkinson’s Disease
rs1806649 (I’m CT)
- C allele – has been identified and may be relevant for breast cancer etiology.
- associated with increased risk of hospital admissions during periods of high PM10 levels
rs1962142 (I’m GG)
- T allele – was associated with a low level of cytoplasmic NRF2 expression (P = 0.036) and negative sulfiredoxin expression (P = 0.042)
- A allele – protected from forearm blood flow (FEV) decline (forced expiratory volume in one second) in relation to cigarette smoking status (p = 0.004)
rs2001350 (I’m TT)
- T allele – protected from FEV decline (forced expiratory volume in one second) in relation to cigarette smoking status (p = 0.004)
rs2364722 (I’m AA)
- A allele – protected from FEV decline (forced expiratory volume in one second) in relation to cigarette smoking status (p = 0.004)
rs2364723
- C allele – associated with significantly reduced FEV in Japanese smokers with lung cancer
rs2706110
- G allele – showed a significant risk for and a protective effect against
drug resistant epilepsy (DRE) - AA alleles – showed significantly reduced KEAP1 expression
- AA alleles – was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (P = 0.011)
rs2886161 (I’m TT)
- T allele – associated with Parkinson’s Disease
rs2886162
- A allele – was associated with low NRF2 expression (P = 0.011; OR, 1.988; CI, 1.162–3.400) and the AA genotype was associated with a worse survival (P = 0.032; HR, 1.687; CI, 1.047–2.748)
rs35652124 (I’m TT)
A allele – associated with higher associated with age at onset for Parkinson’s Disease vs G allele- C allele – had increase NRF2 protein
- T allele – had less NRF2 protein and greater risk of heart disease and blood pressure
rs6706649 (I’m CC)
- C allele – had lower NRF2 protein and increase risk for Parkinson’s Disease
rs6721961 (I’m GG)
- T allele – had lower NRF2 protein
- TT alleles – association between cigarette smoking in heavy smokers and a decrease in semen quality
- TT allele – was associated with increased risk of breast cancer [P = 0.008; OR, 4.656; confidence interval (CI), 1.350–16.063] and the T allele was associated with a low extent of NRF2 protein expression (P = 0.0003; OR, 2.420; CI, 1.491–3.926) and negative SRXN1 expression (P = 0.047; OR, 1.867; CI = 1.002–3.478)
- T allele – allele was also nominally associated with ALI-related 28-day mortality following systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- T allele – protected from FEV decline (forced expiratory volume in one second) in relation to cigarette smoking status (p = 0.004)
- G allele – associated with increased risk of ALI following major trauma in European and African-Americans (odds ratio, OR 6.44; 95% confidence interval
- AA alleles – associated with infection-induced asthma
- AA alleles – exhibited significantly diminished NRF2 gene expression and, consequently, an increased risk of lung cancer, especially those who had ever smoked
- AA alleles – had a significantly higher risk for developing T2DM (OR 1.77; 95% CI 1.26, 2.49; p = 0.011) relative to those with the CC genotype
- AA alleles – strong association between wound repair and late toxicities of radiation (associated with a significantly higher risk for developing late effects in African-Americans with a trend in Caucasians)
- associated with oral estrogen therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism in postmenopausal women
rs6726395 (I’m AG)
A allele – protected from FEV1 decline (forced expiratory volume in one second) in relation to cigarette smoking status (p = 0.004)A allele – associated with significantly reduced FEV1 in Japanese smokers with lung cancer- GG alleles – had higher NRF2 levels and decreased risk of macular degeneration
- GG alleles – had higher survival with Cholangiocarcinoma
rs7557529 (I’m CT)
- C allele – associated with Parkinson’s Disease

Oxidative stress and other stressors can cause cell damage which may eventually lead to a variety of health issues. Research studies have demonstrated that Nrf2 activation can promote the human body’s protective antioxidant mechanism, however, researchers have discussed that Nrf2 overexpression can have tremendous risks towards overall health and wellness. Various types of cancer can also occur with Nrf2 overactivation.
Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Sulforaphane and Its Effects on Cancer, Mortality, Aging, Brain and Behavior, Heart Disease & More
Isothiocyanates are some of the most important plant compounds you can get in your diet. In this
Key sections:
- 00:01:14 – Cancer and mortality
- 00:19:04 – Aging
- 00:26:30 – Brain and behavior
- 00:38:06 – Final recap
- 00:40:27 – Dose
Full timeline:
- 00:00:34 – Introduction of sulforaphane, a major focus of the video.
- 00:01:14 – Cruciferous vegetable consumption and reductions in all-cause mortality.
- 00:02:12 – Prostate cancer risk.
- 00:02:23 – Bladder cancer risk.
- 00:02:34 – Lung cancer in smokers risk.
- 00:02:48 – Breast cancer risk.
- 00:03:13 – Hypothetical: what if you already have cancer? (interventional)
- 00:03:35 – Plausible mechanism driving
the cancer and mortality associative data. - 00:04:38 – Sulforaphane and cancer.
- 00:05:32 – Animal evidence showing
strong effect of broccoli sprout extract on bladder tumor development in rats. - 00:06:06 – Effect of direct supplementation of sulforaphane in prostate cancer patients.
- 00:07:09 – Bioaccumulation of isothiocyanate metabolites in actual breast tissue.
- 00:08:32 – Inhibition of breast cancer stem cells.
- 00:08:53 – History lesson: brassicas were established as having health properties even in ancient Rome.
- 00:09:16 – Sulforaphane’s ability to enhance carcinogen excretion (benzene, acrolein).
- 00:09:51 – NRF2 as a genetic switch via antioxidant response elements.
- 00:10:10 – How NRF2 activation enhances carcinogen excretion via glutathione-S-conjugates.
- 00:10:34 – Brussels sprouts increase glutathione-S-transferase and reduce DNA damage.
- 00:11:20 – Broccoli sprout drink increases benzene excretion by 61%.
- 00:13:31 – Broccoli sprout homogenate increases antioxidant enzymes in the upper airway.
- 00:15:45 – Cruciferous vegetable consumption and heart disease mortality.
- 00:16:55 – Broccoli sprout powder improves blood lipids and overall heart disease risk in type 2 diabetics.
- 00:19:04 – Beginning of
aging section. - 00:19:21 – Sulforaphane-enriched diet enhances
lifespan of beetles from 15 to 30% (in certain conditions). - 00:20:34 – Importance of low inflammation for longevity.
- 00:22:05 – Cruciferous vegetables and broccoli sprout powder seem to reduce a wide variety of inflammatory markers in humans.
- 00:23:40 – Mid-video recap: cancer, aging sections
- 00:24:14 – Mouse studies suggest sulforaphane might improve adaptive immune function in old age.
- 00:25:18 – Sulforaphane improved hair growth in a mouse model of balding.
Picture at 00:26:10. - 00:26:30 – Beginning of brain and behavior section.
- 00:27:18 – Effect of broccoli sprout extract on autism.
- 00:27:48 – Effect of glucoraphanin on schizophrenia.
- 00:28:17 – Start of depression discussion (plausible mechanism and studies).
- 00:31:21 – Mouse study using 10 different models of stress-induced depression show sulforaphane similarly effective as fluoxetine (
prozac ). - 00:32:00 – Study shows direct ingestion of glucoraphanin in mice is similarly effective at preventing depression from social defeat stress model.
- 00:33:01 – Beginning of neurodegeneration section.
- 00:33:30 – Sulforaphane and Alzheimer’s disease.
- 00:33:44 – Sulforaphane and Parkinson’s disease.
- 00:33:51 – Sulforaphane and Hungtington’s disease.
- 00:34:13 – Sulforaphane increases heat shock proteins.
- 00:34:43 – Beginning of traumatic brain injury section.
- 00:35:01 – Sulforaphane injected immediately after TBI improves memory (mouse study).
- 00:35:55 – Sulforaphane and neuronal plasticity.
- 00:36:32 – Sulforaphane improves learning in
model of type II diabetes in mice. - 00:37:19 – Sulforaphane and
duchenne muscular dystrophy. - 00:37:44 – Myostatin inhibition in muscle satellite cells (in vitro).
- 00:38:06 – Late-video recap: mortality and cancer, DNA damage, oxidative stress and inflammation, benzene excretion, cardiovascular disease, type II diabetes, effects on the brain (depression, autism, schizophrenia, neurodegeneration), NRF2 pathway.
- 00:40:27 – Thoughts on figuring out a dose of broccoli sprouts or sulforaphane.
- 00:41:01 – Anecdotes on sprouting at home.
- 00:43:14 – On cooking temperatures and sulforaphane activity.
- 00:43:45 – Gut bacteria conversion of sulforaphane from glucoraphanin.
- 00:44:24 – Supplements work better when combined with active myrosinase from vegetables.
- 00:44:56 – Cooking techniques and cruciferous vegetables.
- 00:46:06 – Isothiocyanates as goitrogens.
According to research studies,
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez

Additional Topic Discussion: Acute Back Pain
Back pain is one of the most prevalent causes of disability and missed days at work worldwide. Back pain attributes to the second most common reason for doctor office visits, outnumbered only by upper-respiratory infections. Approximately 80 percent of the population will experience back pain at least once throughout their life. The spine is a complex structure made up of bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles, among other soft tissues. Injuries and/or aggravated conditions, such as herniated discs, can eventually lead to symptoms of back pain. Sports injuries or automobile accident injuries are often the most frequent cause of back pain, however, sometimes the simplest of movements can have painful results. Fortunately, alternative treatment options, such as chiropractic care, can help ease back pain through the use of spinal adjustments and manual manipulations, ultimately improving pain relief.

EXTRA EXTRA | IMPORTANT TOPIC: Recommended El Paso, TX Chiropractor
***
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "What Are The Risks Of Nrf2 Overexpression?" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics



 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.