Tendons and Ligaments: A tendon is a fibrous flexible, strong tissue similar to a rope that attaches the muscles to the bones. Tendons allow for the movement of the body’s limbs and help prevent muscle injury by absorbing muscles’ impact when running, jumping, or performing other actions. Ligaments are bands of solid elastic tissue that connect bone to bone, hold structures together and keep them stable, support the joints and limit their movement.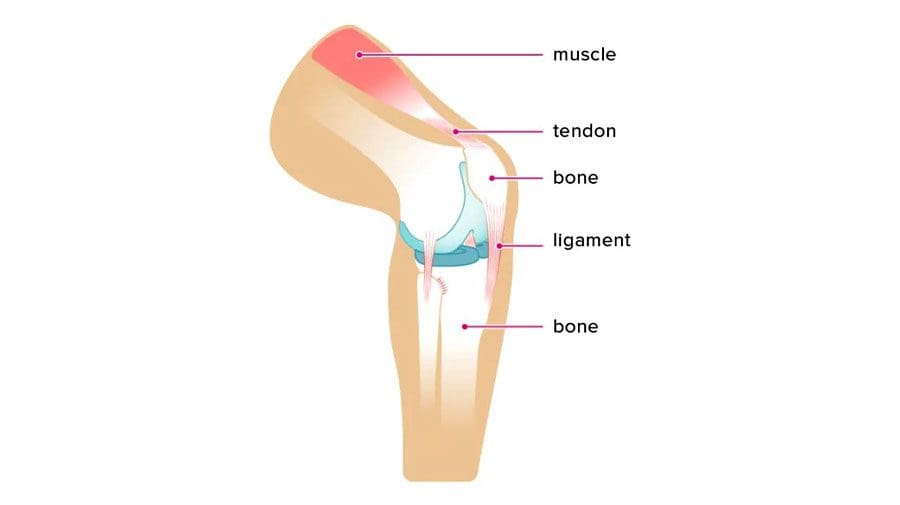
Table of Contents
Tendons and Ligaments
- Tendons are strong and non-flexible.
- Ligaments are flexible and elastic.
- Both comprise collagen and living cells, essential in joints and bones and integral to locomotion.
- Tendons allow body movement by transmitting force from muscle to bone, allowing the body to stand, walk, and jump.
- Ligaments work by allowing for the full range of motion.
- Ligaments are around the knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders, and other joints.
Connective Tissue
- The collagen connective tissue that makes up tendons and ligaments is the same; their patterns are different.
- Tendon fibers are laid out in a parallel pattern.
- Tendon connective tissue needs to have more elasticity to help move the muscles.
- Ligament fibers are laid out in a crisscross pattern.
- Ligament connective tissue stabilizes and strengthens the bones’ joint structure.
Tendon Injury
A tendon that gets overstretched or torn is known as a strain. Common areas affected by strains are the:
- Leg
- Foot
- Back
Strains often result from repetitive work movements, intense physical activity, and sports. Individuals who overuse their bodies without proper rest and muscle repair recovery have an increased risk of injury. Symptoms include:
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Pain
- Cramping
- Weakness
Ligament Injury
A ligament that gets overstretched or torn results in a sprain. Sprains can happen suddenly from a fall, awkward movement, or trauma. Sprains commonly occur in the:
- Ankle
- Knee
- Wrist
Examples include:
- Misstep causing the ankle to twist in an awkward position, snapping a ligament and causing unstableness or wobbliness.
- There could be a popping sensation or the feeling of a tear when the injury occurs.
- Wrist sprains often happen when reaching out and extending the hands to break a fall, and the wrist hyperextending back.
- The hyperextension overstretches the ligament.
Symptoms of a sprained ligament include:
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Pain
- The joint may feel loose or weak and unable to take on weight.
The intensity of symptoms varies depending on whether the ligament is overextended or torn. Sprains are classified by grade:
- Grade 1 – a mild sprain with slight stretching of the ligament.
- Grade 2 – a moderate ligament tear, but not a complete tear.
- Grade 3 – a complete ligament tear, making the joint unstable.
Chiropractic Care
Tendons and ligaments do not receive full blood circulation like other soft tissues. Depending on the severity of the injury, and the slower transfer of oxygen and nutrients, ligament and tendon injuries can take six to twelve weeks to heal, and repeatedly stressing the injured area from overuse can extend recovery. Chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy, combined with corrective exercises and stretches, will reduce inflammation, decrease pain, improve the range of motion, increase nerve and muscle function, and strengthen the muscles. Chiropractic treatment involves:
- Soft tissue work
- Percussive massage
- Cross friction massage
- Deep tissue massage
- Trigger point therapy
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
- Ultrasound
- Anti-inflammatory nutritional recommendations
Knee Injuries Adjustment
References
Childress, Marc A, and Anthony Beutler. “Management of chronic tendon injuries.” American family physician vol. 87,7 (2013): 486-90.
Fenwick, Steven A et al. “The vasculature and its role in the damaged and healing tendon.” Arthritis research vol. 4,4 (2002): 252-60. doi:10.1186/ar416
Leong, Natalie L et al. “Tendon and Ligament Healing and Current Approaches to Tendon and Ligament Regeneration.” Journal of orthopedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society vol. 38,1 (2020): 7-12. doi:10.1002/jor.24475
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/sprains-strains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries
Scalcione, Luke R et al. “The athlete’s hand: ligament and tendon injury.” Seminars in musculoskeletal radiology vol. 16,4 (2012): 338-49. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1327007
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Tendons and Ligaments Injuries Chiropractic Scientist" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics



 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.