The latissimus dorsi or lats are the large flat muscles on each side covering the width of the middle and lower back. They connect the bone of the upper arm to the spine and the hip. When pain presents in these muscles, it is typically caused by:
- Repetitive overuse in a job or doing a task/chore that requires constant
- Bending
- Pulling
- Pushing
- Reaching
- Twisting
- Kneeling
- A result of poor technique in sports or similar physical activities.
Chiropractic treatment, along with exercises, can help prevent and relieve this pain.
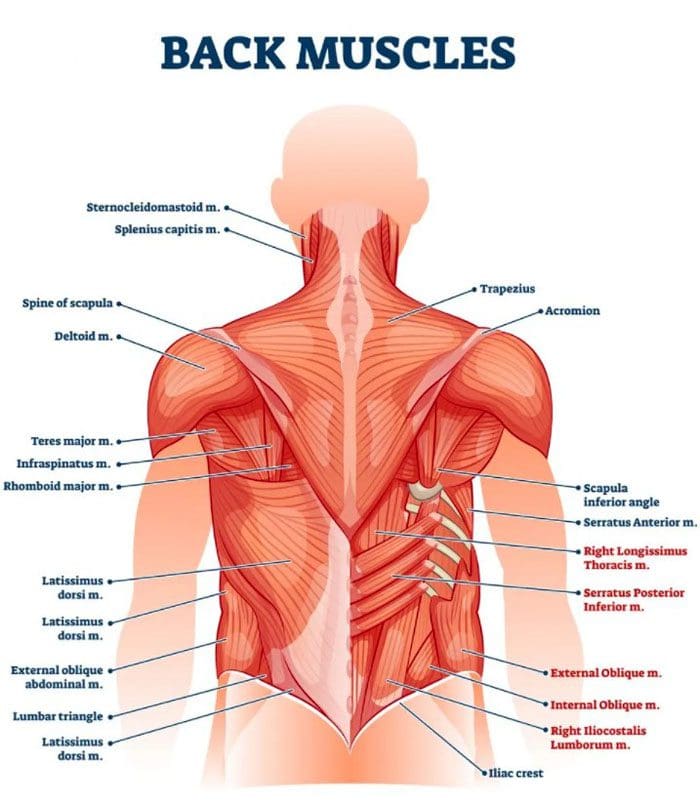
Table of Contents
Symptoms of lat pain
The objective is to diagnose whether the pain is located in the latissimus dorsi or other muscles in the shoulders or back. If the latissimus dorsi is injured, an individual might feel pain in several areas, these include:
- Lower, middle, and upper back
- Back of the shoulders
- The base of the shoulder blade
- Lower arms
- Inside of the arms, extending down to the fingers
In certain cases, the pain will present without warning and can be felt in the surrounding muscles. This type of pain often gets worse when the individual:
- Extends their hands forward and out in front
- Raises their hands above their head
- Tosses or throws an object
Damage or injury to the latissimus dorsi
Tissue damage or injury can cause other symptoms to present. These include:
- Tingling in the lower arms
- Breathing causes aching and/or pain
- Tendonitis in the middle and/or lower back
If the source of the back pain cannot be identified, or if it is accompanied by:
- Fever
- Breathing problems
- Abdominal pain
- Consult a doctor as these could be symptoms of a more serious condition.
Uses and Causes
The lat muscles are used in everyday activities. These include:
- Picking up objects like grocery bags
- Opening heavy doors
- Chest expansion for breathing
- Pushing against the armrests of a chair to stand up
- Using handrails to climb stairs
For sports or working out, the lats are used in:
- Weightlifting exercises using the upper body
- Bench-presses
- Rowing
- Swimming
- Throwing
Common causes of pain include:
- Overusing the muscles
- Using poor techniques
- Exercising without warming up
Risk of injury
Individuals that are at risk of developing this injury include those that:
- Are continually reaching overhead
- Regularly chop wood
- Perform regular shoveling
- Move furniture or other heavy objects
- Regularly practice poor posture
Tearing the latissimus dorsi is possible, especially for athletes. Some athletes with increased risk include:
- Golfers
- Baseball pitchers
- Gymnasts
- Swimmers
- Tennis players
Exercises that can help bring relief
Certain exercises can alleviate the aches, pain, and strengthen the lat muscles to prevent and/or worsen the injury. It is recommended to consult a doctor, sports chiropractor, or personal trainer before beginning a therapeutic exercise regimen. This is to ensure that the exercises are right for the individual and their condition and that they use the correct form. Here are two exercises that can help reduce the pain. The doctor, chiropractor, or trainer will recommend the frequency the individual should perform the exercises.
Back bow
This pose is known as the superman pose. To perform:
- Lay facedown on the floor
- Extend the legs so they are straight
- Stretch arms away from the body, so they are in front of the head
- Use the back to raise the shoulders
- Extend the arms and legs upward
- Hold the position for 10 seconds
Pelvic raise/lift
To perform this exercise:
- Lay flat on your back with the arms at the sides
- Bend the knees like for a sit-up with the heels close to the buttocks
- Keeping the hands and feet in place
- Lift the pelvis upward
- Slowly lower back to the floor
Prevention
Individuals can prevent lat pain with lifestyle adjustments. These include:
- Using proper technique and posture during work, sports, and exercise
- Staying aware to not overuse the muscles
- Staying hydrated
- Warming up and cooling down thoroughly before and after a workout, sports, physical activities
- Regular stretching
- Applying ice and heat before and after work, sports, and physical activities
- Chiropractic care
- Physical therapy massage
Body Composition
Nutrition and Recovery Advantage
Two important steps to achieve optimal health include:
Nutrition
Having a proper protein intake is important for muscle adaptability or the way muscles adapt to stress during exercise and/or strength training. This is also important to stimulate muscle protein synthesis after exercising and/or strength training. To ensure the body is getting the strength and hypertrophy improvement from exercise and strength training, it is recommended to eat around 25g of high-quality protein after workout sessions.
Recovery
For those doing aerobic and strength training, maximize recovery time between workout sessions. This is because strength and aerobic fitness health gains are low when the two only have a separation of 6 hours or less. Twenty-four hours between sessions is recommended especially if the priority is endurance performance.
References
Anderson, S. E., Hertel, R., Johnston, J. O., Stauffer, E., Leinweber, E., & Steinbach, L. S. (2005, November). Latissimus dorsi tendinosis and tear: imaging features of a pseudotumor of the upper limb in five patients. American Journal of Roentgenology, 185(5), 1145–1151
https://www.ajronline.org/doi/abs/10.2214/AJR.04.1247
Donohue, Benjamin F et al. “Sports Injuries to the Latissimus Dorsi and Teres Major.†The American journal of sports medicine vol. 45,10 (2017): 2428-2435. doi:10.1177/0363546516676062http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0363546516676062?journalCode=ajsb
Henseler, J. F., Nagels, J., Nelissen, R. G. H. H., & de Groot, J. H. (2014, April). Does the latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for massive rotator cuff tears remain active postoperatively and restore active external rotation? Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 23(4), 553–560
http://www.jshoulderelbow.org/article/S1058-2746(13)00399-6/fulltext%20
George, Michael S, and Michael Khazzam. “Latissimus Dorsi Tendon Rupture.†The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons vol. 27,4 (2019): 113-118. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00581
Lehman, Gregory J et al. “Variations in muscle activation levels during traditional latissimus dorsi weight training exercises: An experimental study.†Dynamic medicine: DM vol. 3,1 4. 30 Jun. 2004, doi:10.1186/1476-5918-3-4
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Straining, Spasming, Injuring The Lat Muscles" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics




 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.