Table of Contents
Introduction
The elbows and the forearms have a casual relationship with each other as they provide flexion and retraction of the arms in the body. Each different muscle group in the body has the job of making the body functional. The arms help the body to carry items while the shoulders provide stability to the head and neck. The head and neck work together to allow rotation and movement. Finally, the legs and hips stabilize the body’s upper half and move from place to place. Traumatic events or injuries that affect the arms can lead to pain along the muscles in the forearms. This can lead to the muscles becoming inflamed and developing myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points along the affected muscles. One of the muscles in the forearms that can be affected by myofascial pain syndrome is the supinator muscles. Today’s article looks at the supinator muscles, how myofascial pain affects the supinator muscles, and how to manage myofascial pain syndrome along the supinator muscles. We refer patients to certified providers who specialize in elbow pain treatments to aid individuals suffering from myofascial pain syndrome associated with the supinator muscles near the elbow and forearm. We also guide and inform our patients by referring them to our associated medical providers based on their examination when appropriate. We established that education is a great solution to asking our providers profound questions the patient requests. Dr. Jimenez DC takes note of this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
What Is The Supinator Muscle?
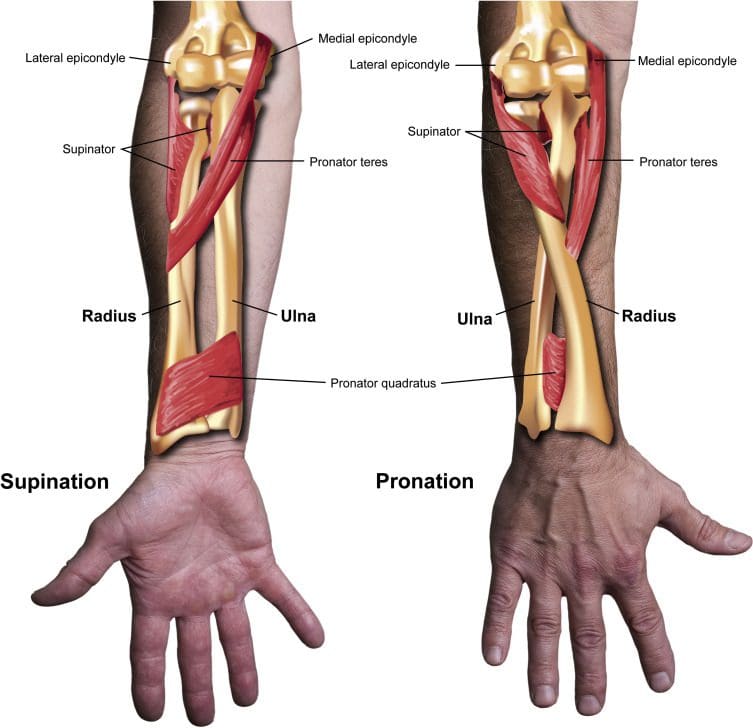
Are you experiencing any pain along your forearm or elbow? What about feeling stiffness along your thumb? Do you feel any tenderness or soreness in your forearm muscle? People who have been experiencing these symptoms might be dealing with myofascial pain syndrome that is affecting their supinator muscles. According to Dr. Travell, M.D.’s book, “Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual,” the supinator muscle is a flat spiral muscle under the elbow joint and is located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. The supinator muscle function is to supinate or turn the forearm when the elbow is in a position of flexion or extension. The supinator muscle also works together with the bicep brachii muscles. Studies reveal that the biceps function provides stability and assists with internal rotation with the elbow joint by interacting with the supinator muscle. Both of these muscles provide supination and flexion strength to the elbow. However, the supinator muscle can also be affected by injuries in the elbows and forearms, causing referred pain along the forearms and parts of the hand, primarily the thumb.
Myofascial Pain Affecting The Supinator Muscle
When the supinator muscle is suffering from pain, various issues can cause the pain to occur near the elbow and forearm. Multiple factors can include:
- Carrying a large, heavy bag.
- Playing tennis.
- Extreme movements cause the elbow to be hyperextended and lead to myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points along the supinator muscles.
Now tennis elbow is often associated with trigger points as it affects the lateral head of the triceps and the extensor muscles next to the supinator muscles. Studies reveal that tennis elbow usually occurs on the dominant arm and is regarded as an overuse injury that involves repetitive extension against resistance. To that point, the repetitive motions can lead to the development of trigger points along the supinator muscles.
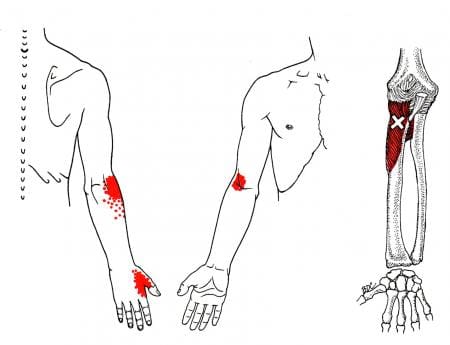
Many people with active trigger points in the supinator muscles often complain about twinges of pain located in the front or back of the elbow, along with muscle tenderness in the supinator muscle. Myofascial pain syndrome can also mimic other chronic pain conditions in the arm that causes referred pain symptoms associated with the muscle. Myofascial pain syndrome causes the affected muscle to be hyperirritable and causes the surrounding nerves that are intertwined with the muscles to be compressed. This causes various symptoms in the forearms, like tingling sensations, numbness, and a decrease in grip strength. All is not lost as multiple ways to manage myofascial pain syndrome along the supinator muscles.
How To Release Supinator Trigger Points- Video
Are you experiencing twinges of pain near your elbow? What about radiating pain along your thumb? Do you feel tenderness or muscle weakness on your forearms or your elbow? Many of these symptoms are due to the development of myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points that are affecting the supinator muscles. Trigger points can mimic other chronic pain conditions that can cause referred pain to the rest of the body. The video above explains where trigger points are located in the supinator muscle and how to release the trigger points from that muscle. Various techniques can help manage myofascial pain syndrome that is affecting the supinator muscles and can help alleviate the pain-like symptoms that are along the muscle fibers.
Managing Myofascial Pain Syndrome Along The Supinator Muscles

When managing myofascial pain syndrome along the supinator muscles, many individuals can incorporate these techniques as part of their daily activities. Many individuals can go to a pain specialist that targets myofascial pain syndrome through palpations and massages. Studies reveal that incorporating a diagnosis of where the palpations have occurred and massaging the affected muscle can release the trigger points from the muscle and reduce pain. Another technique many people can utilize to manage myofascial pain syndrome is not overextending the elbow to cause trigger points to form. This is extremely important for tennis players to prevent tennis elbows from forming and reduce the chances of trigger points forming along the supinator muscles. And lastly, doing isotonic exercises can help strengthen and condition the supinator muscles to prevent injuries. These techniques allow the individual to be pain-free and continue with their daily lives.
Conclusion
The supinator muscles are located underneath the elbow, allowing forearm rotation when the elbow is flexed or extended. When the supinator muscle is affected by injuries or repetitive motions, it can develop trigger points or myofascial pain syndrome. This causes referred pain along the elbow to parts of the hand, primarily the thumb. Trigger points can even overlap and cause symptoms of “tennis elbow” to cause pain along the muscle and joints. Luckily, various techniques can prevent trigger points from developing further and reduce the pain in the elbows and forearms. To that point, the individual can continue doing their daily activities.
References
Bron, Carel, et al. “Interrater Reliability of Palpation of Myofascial Trigger Points in Three Shoulder Muscles.” The Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, Inc., 2007, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2565638/.
Cutts, S, et al. “Tennis Elbow: A Clinical Review Article.” Journal of Orthopaedics, Elsevier, 10 Aug. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6926298/.
Güleçyüz, Mehmet F, et al. “Reference Values of Flexion and Supination in the Elbow Joint of a Cohort without Shoulder Pathologies.” BioMed Research International, Hindawi, 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5674724/.
Travell, J. G., et al. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual: Vol. 1:Upper Half of Body. Vol. 1, Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Myofascial Pain Syndrome Affecting The Supinator Muscles" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness, Personal Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, and focuses on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card



 Again, We Welcome You.
Again, We Welcome You.
Comments are closed.